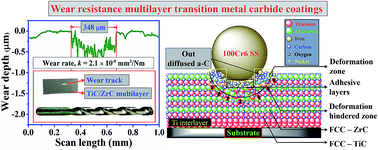
To enhance the performance and durability of mechanical components, surface properties need to be modified. In this work, a unique combination of transition metal carbide (TMC) multilayer coatings (TiC/CrC, TiC/ZrC and TiC/WC) were deposited by reactive DC magnetron sputtering on 316LN steel substrates. GIXRD results showed the presence of an amorphous CrC phase in the TiC/CrC multilayer, whereas, crystalline TiC, ZrC and W2C phases were observed in their respective coatings. FESEM analysis indicated the non-columnar structures of TMC layers in all the samples, except the CrC layer in the TiC/CrC multilayer. Solid solutions of the TiC and WC layers at the interface were identified due to the migration of W atoms into the TiC crystal lattices. The poor crystalline nature of the TiC/CrC multilayer led to lower hardness and weak wear resistance. However, enhanced tribo-mechanical properties were observed in TiC/ZrC and TiC/WC multilayer coatings. This is explained by the improved crystallinity and enhanced resistance to plastic deformation. For the selected tribological parameters, abrasive, adhesive and combined abrasive/adhesive wear modes are the major governing factors in determining the wear behaviors of TiC/CrC, TiC/ZrC and TiC/WC coatings, respectively. The chemical stability of deformed wear tracks was observed by Raman spectroscopy.