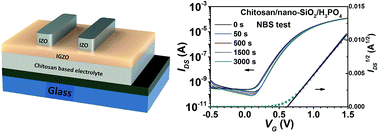
In this article, we report on the successful implementation of nanoparticle incorporation and acid doping in tuning the properties of chitosan for proton-based ion gating of metal–oxide electric double layer transistors (EDLTs). SiO2 nanoparticle (nano-SiO2) incorporation was initially found to produce rougher surfaces, lower the specific capacitance and postpone the transport of protons, which deteriorated the performance of the transistors. The advantage of nano-SiO2 incorporation lies in their ability to significantly improve the transistor's negative bias stability due to a proposed proton blocking mechanism. By applying doping of H3PO4, the negative effects of nano-SiO2 incorporation were partially counterbalanced. This is because H3PO4 can donate more protons and assist the proton conduction via the donor/acceptor process of amphoteric acids or forming the molecular network of hydrogen bonds. Overall, this work presents a promising strategy to optimize the bio-polyelectrolyte gated EDLTs by combining nanoparticle incorporation and acid doping.