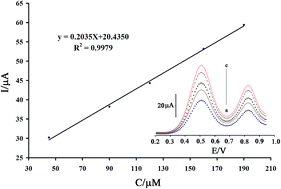
Cyclic voltammetry (CV), square wave voltammetry (SWV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and double potential step chronoamperometry were used to investigate the electrochemical oxidation of glutathione (GSH) at a chemically modified electrode prepared by incorporating acetylferrocene (AF) and NiO nanoparticles (NiO/NPs) into a carbon paste matrix. For the mixture containing GSH and vitamin B6, the peak potentials were well separated from each other. Under optimal conditions in cyclic voltammetry, linear ranges spanned a GSH concentration from 0.2 μM to 350.0 μM and the detection limit was 0.09 μM at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3. The novel sensor was successfully used for the voltammetric determination of the GSH in real samples with satisfactory results.