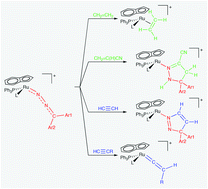
Diazoalkane complexes [Ru(η5-C9H7)(N2CAr1Ar2)(PPh3)L]BPh4 (1–3) [L = PPh3, P(OMe)3, P(OEt)3; Ar1 = Ar2 = Ph; Ar1 = Ph, Ar2 = p-tolyl; Ar1Ar2 = C12H8 fluorenyl] were prepared by allowing chloro-complexes [RuCl(η5-C9H7)(PPh3)L] to react with an excess of diazoalkane in ethanol. Complexes 1–3 reacted with ethylene CH2![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 (1 atm) and maleic anhydride [ma, CH
CH2 (1 atm) and maleic anhydride [ma, CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCO(O)CO] to afford η2-alkene complexes [Ru(η5-C9H7)(η2-CH2
CHCO(O)CO] to afford η2-alkene complexes [Ru(η5-C9H7)(η2-CH2![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2)(PPh3)L]BPh4 (4, 5) and [Ru(η5-C9H7){η2-CH
CH2)(PPh3)L]BPh4 (4, 5) and [Ru(η5-C9H7){η2-CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCO(O)CO}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (7). Further, complexes 1–3 underwent cycloaddition with acrylonitrile CH2
CHCO(O)CO}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (7). Further, complexes 1–3 underwent cycloaddition with acrylonitrile CH2![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(H)CN, giving 1H-pyrazoline derivatives [Ru(η5-C9H7){η1-N
C(H)CN, giving 1H-pyrazoline derivatives [Ru(η5-C9H7){η1-N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(CN)CH2C(Ar1Ar2)NH}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (6). Treatment of diazoalkane complexes 1–3 with acetylene CH
C(CN)CH2C(Ar1Ar2)NH}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (6). Treatment of diazoalkane complexes 1–3 with acetylene CH![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CH under mild conditions (1 atm, room temperature) led to dipolar cycloaddition, affording 3H-pyrazole complexes [Ru(η5-C9H7)-{η1-N
CH under mild conditions (1 atm, room temperature) led to dipolar cycloaddition, affording 3H-pyrazole complexes [Ru(η5-C9H7)-{η1-N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NC(Ar1Ar2)CH
NC(Ar1Ar2)CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (8), whereas reaction with terminal alkynes RC
CH}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (8), whereas reaction with terminal alkynes RC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CH (R = Ph, p-tolyl, But) gave vinylidene derivatives [Ru(η5-C9H7){
CH (R = Ph, p-tolyl, But) gave vinylidene derivatives [Ru(η5-C9H7){![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(H)R}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (9). The latter reacted with nucleophiles such as amines and alcohols to give amino- and alkoxy-carbene derivatives [Ru(η5-C9H7){
C(H)R}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (9). The latter reacted with nucleophiles such as amines and alcohols to give amino- and alkoxy-carbene derivatives [Ru(η5-C9H7){![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(NHPrn)(CH2Ph)}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (11) and [Ru(η5-C9H7){
C(NHPrn)(CH2Ph)}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (11) and [Ru(η5-C9H7){![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(CH3)(OEt)}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (10), respectively. In addition, complexes 9 reacted with phenylhydrazine to afford nitrile derivatives [Ru(η5-C9H7)(N
C(CH3)(OEt)}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (10), respectively. In addition, complexes 9 reacted with phenylhydrazine to afford nitrile derivatives [Ru(η5-C9H7)(N![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CCH2R)(PPh3)L]BPh4 (12) and phenylamine, whereas the reaction with water led to hydrolysis of the alkyne and formation of carbonyl complexes [Ru(η5-C9H7)(CO)(PPh3)L]BPh4 (13). Lastly, treatment of vinylidene complexes 9 with the phosphines PPh3 and P(OMe)3 afforded alkenylphosphonium derivatives [Ru(η5-C9H7){C(H)
CCH2R)(PPh3)L]BPh4 (12) and phenylamine, whereas the reaction with water led to hydrolysis of the alkyne and formation of carbonyl complexes [Ru(η5-C9H7)(CO)(PPh3)L]BPh4 (13). Lastly, treatment of vinylidene complexes 9 with the phosphines PPh3 and P(OMe)3 afforded alkenylphosphonium derivatives [Ru(η5-C9H7){C(H)![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(R)PPh3}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (14) and [Ru(η5-C9H7){C(R)
C(R)PPh3}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (14) and [Ru(η5-C9H7){C(R)![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(H)P(OMe)3}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (15), respectively. Compound [Ru(η5-C9H7){C(H)
C(H)P(OMe)3}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (15), respectively. Compound [Ru(η5-C9H7){C(H)![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(H)PPh3}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (16) was also prepared. The complexes were characterised by spectroscopy (IR and NMR) and X-ray crystal structure determinations of [Ru(η5-C9H7){N2C(C12H8)}(PPh3){P(OEt)3}]BPh4 (3c), [Ru(η5-C9H7){
C(H)PPh3}(PPh3)L]BPh4 (16) was also prepared. The complexes were characterised by spectroscopy (IR and NMR) and X-ray crystal structure determinations of [Ru(η5-C9H7){N2C(C12H8)}(PPh3){P(OEt)3}]BPh4 (3c), [Ru(η5-C9H7){![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(H)Ph}(PPh3){P(OEt)3}]BPh4 (9d) and [Ru(η5-C9H7){C(H)
C(H)Ph}(PPh3){P(OEt)3}]BPh4 (9d) and [Ru(η5-C9H7){C(H)![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(Ph)PPh3}(PPh3){P(OEt)3}]BPh4 (14d).
C(Ph)PPh3}(PPh3){P(OEt)3}]BPh4 (14d).