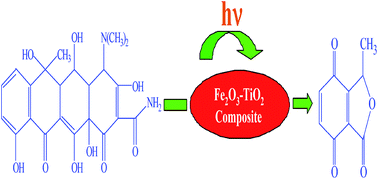
The degradation behavior of oxytetracycline (OTC) in aqueous solution using Fe2O3–TiO2 nanopowders (Fe2O3–TiO2 NPs) as photocatalysts under UV/visible light was investigated in this paper. Fe2O3–TiO2 NPs photocatalysts synthesized using co-precipitation were characterized by XRD, TEM, FT-IR and UV-vis DRS. Fe2O3–TiO2 NPs with 45 wt% Fe2O3 exhibited higher photocatalytic activity than others. The photocatalytic degradation of OTC shows a maximum efficiency at pH = 5.5 under both UV/visible light due to the surface adsorption. The intermediate products during the photocatalytic degradation of OTC were detected by LC-MS/TOF. Seven main intermediates were formed, and their evolution was discussed. On the basis of the evidence oxidative intermediate formation and a detailed degradation path way of OTC by 45 Fe2O3–TiO2 NPs are proposed.