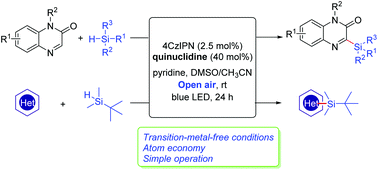
Direct C–H silylation of quinoxalinones was achieved by the combination of organic photoredox catalysis and hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) under ambient air conditions. Transition metal- and external oxidant-free conditions were the major features of this protocol. A series of silylated quinoxalinones with broad functional groups had been synthesized in moderate to high yields. This methodology was also applicable for the C–H silylation of some electron-deficient heteroarenes.