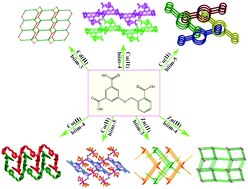
A series of coordination polymers based on 5-(2-carboxybenzyloxy) isophthalic acid and bis(imidazole) ligands, namely, [Cd(HL)(biim-3)]·5H2O (1), [Zn2(HL)2(biim-3)2]·3H2O (2), [Zn(HL)(biim-4)] (3), [Co(HL)(biim-4)] (4), [Co(HL)(biim-5)2]·6.75H2O (5), [Cu(HL)(biim-4)] (6) and [Cu(HL)(biim-5)] (7), where H3L = 5-(2-carboxybenzyloxy) isophthalic acid, biim-3 = 1,1′-(1,3-propanediyl)bis(imidazole), biim-4 = 1,1′-(1,4-butanediyl)bis(imidazole) and biim-5 = 1,1′-(1,5-pentanediyl)bis(imidazole), have been synthesized under hydrothermal conditions. Their structures have been determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analyses and further characterized by infrared spectra (IR), elemental analyses and powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) analyses. In compounds 1–7, the H3L ligands are partially deprotonated to form the HL2− anion. Compound 1 displays a 2D layer structure with (3,4)-connected (42·6)(43·62·8) topology. Compound 2 exhibits an unusual 2D → 3D polythreaded framework. Compound 3 is a 3D framework with 4-connected (65·8) topology. Compound 4 is an unusual 2D → 2D interdigitated double layer formed by C–H⋯π interactions, which is further stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen bonding interactions. Compound 5 is a double chain structure. The intermolecular hydrogen bonding interactions further connected the chains to form a 3D supramolecular architecture. Compound 6 is a 2D layer structure, which is further extended by the intermolecular hydrogen-bonding interactions to form a 3D supramolecular framework. Compound 7 is an unusual 1D → 3D interdigitated framework.