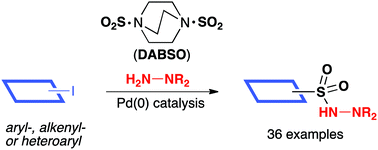
By using DABCO·(SO2)2, DABSO, as a solid bench-stable SO2-equivalent, the palladium-catalysed aminosulfonylation of aryl-, alkenyl- and heteroaryl halides has been achieved. N,N-Dialkylhydrazines are employed as the N-nucleophiles and provide N-aminosulfonamides as the products in good to excellent yields. The reactions are operationally simple to perform, requiring only a slight excess of SO2 (1.2–2.2 equiv.), and tolerate a variety of substituents on the halide coupling partner. Variation of the hydrazine component is also demonstrated. The use of N,N-dibenzylhydrazine as the N-nucleophile delivers N-aminosulfonamide products that can be converted into the corresponding primary sulfonamides using a high-yielding, telescoped, deprotection sequence. The ability to employ hydrazine·SO2 complexes as both the N-nucleophile and SO2 source is also illustrated.