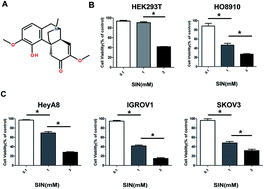
Sinomenine (SIN), an isoquinoline isolated from the Chinese medicinal plant Sinomenium acutum, is well known for its curative effect on rheumatic and arthritic diseases. Recently, SIN has been reported to possess potent anti-tumor effects in various types of cancers. However, the role and the underlying mechanism of the inhibitory action of SIN on ovarian cancer remain unknown. In this study, we preliminarily found that SIN might suppress tumor proliferation and metastasis by modulating the oncogene MCM2 and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The results demonstrated that SIN could inhibit ovarian cancer cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. IGROV1 or HeyA8 cells treated with 0.25 mM, 0.5 mM, and 1 mM SIN exhibited gradually reduced growth capacity. Correspondingly, the protein expression levels of c-myc and cyclinD1 were also obviously decreased. In addition, reduction in migration and invasion rates was found in IGROV1 or HeyA8 cells treated with 0.25 mM and 0.5 mM SIN. Western blot results revealed that SIN could upregulate the protein expression levels of epithelial markers such as ZO-1 and E-cadherin; it also downregulated the protein expression levels of mesenchymal markers, i.e., vimentin, N-cadherin, ZEB1, and Snail. Furthermore, Wnt/β-catenin signaling attenuation was followed by the suppression of total β-catenin, cytoplasmic β-catenin, and nuclear β-catenin due to SIN treatment. MCM2 was verified to exhibit a positive relation with ovarian cancer malignancy in 75 ovarian cancer tissue and 15 paracancer tissue samples. Furthermore, MCM2 could be reduced by SIN, and its overexpression could rescue the loss of β-catenin, ZEB1, c-myc, and cyclinD1 mRNA levels together with β-catenin and ZEB1 protein expression levels, which could markedly be inhibited by MCM2 knockdown again. In summary, SIN might play anti-proliferation and anti-metastasis functions in ovarian cancer via targeting MCM2 and thereby regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Thus, it could be considered to be a promising chemopreventive compound to treat ovarian carcinoma.