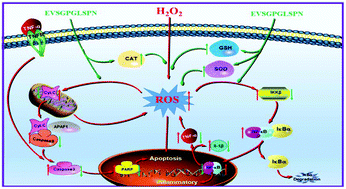
Amelioration of oxidative stress has been the main approach to improve neurodegenerative disorders. In the present study, a walnut peptide with a strong capacity of scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) was purified and identified as EVSGPGLSPN by SEC, RP-HPLC, and HPLC-MS/MS. Treatment with EVSGPGLSPN could significantly (P < 0.05) reduce ROS generation, and increase cell viability, and superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-px) activities in a dose-dependent manner in hydrogen peroxide induced PC12 cells. Western blot and immunofluorescence analysis showed that EVSGPGLSPN suppressed the expression of IKKβ and p65 to inhibit NF-κB pathway activation, attenuating the neurotoxic cascade by overexpression of IL-1β and TNF-α. Moreover, EVSGPGLSPN inhibited apoptosis by suppressing the expression of cytochrome C, caspase-9, caspase-3, and PARP. Additionally, it also up-regulated the expression of p-CREB and synaptophysin in oxidatively damaged PC12 cells. Thus, EVSGPGLSPN may protect against hydrogen peroxide induced neurotoxicity by enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes and blocking the NF-κB/caspase pathways.