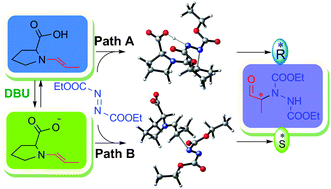
The transition state models in two mechanistically distinct pathways, involving (i) an enamine carboxylic acid (path-A, 4) and (ii) an enamine carboxylate (path-B, 8), in the proline-catalyzed asymmetric α-amination have been examined using DFT methods. The path-A predicts the correct product stereochemistry under base-free conditions while path-B accounts for reversal of configuration in the presence of a base.