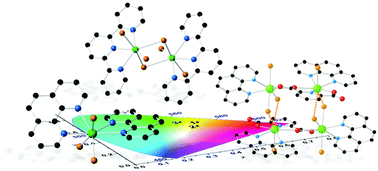
Three bismuth(III)-organic compounds, [Bi4Cl8(PDC)2(phen)4]·2MeCN (1), [BiCl3(phen)2] (2), and [Bi2Cl6(terpy)2] (3), were prepared from solvothermal reactions of bismuth chloride, 2,6-pyridinedicarboxylic acid (H2PDC), and 1,10-phenanthroline (phen) or 2,2′;6′,2′′-terpyridine (terpy). The structures were determined through single crystal X-ray diffraction and the compounds were further characterized via powder X-ray diffraction, Raman and infrared spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis. The photoluminescence properties of the solid-state materials were assessed using steady state and time-dependent techniques to obtain excitation and emission profiles as well as lifetimes. The compounds exhibit visible emission ranging from the yellow-green to orange region upon UV excitation. Theoretical quantum mechanical calculations aimed at elucidating the observed emissive behavior show that the transitions can be assigned as predominantly ligand-to-ligand and ligand-to-metal charge transfer transitions. The solid-state structural chemistry, spectroscopic properties, and luminescence behavior of the bismuth compounds are presented herein.