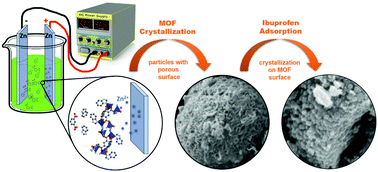
In this paper, mixed-ligand Zn-based metal–organic framework [Zn(1,3-bdc)0.5(bzim)] was synthesized via the electrochemical method. Studies on different synthesis parameters demonstrated that the time of reaction and the current density were the most significant factors affecting the purity and yield of the product. We found that the best conditions to obtain pure-phase MOF with high yield (87%) were a 60 mA current and a 2 h reaction time. The applied synthesis conditions allowed the reaction time and size of the crystallites to be significantly reduced when compared to the conventional solvothermal, hydrothermal or diffusion methods. The most promising sample was fully characterized by Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD), Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Thermogravimetry (TG), and surface area measurement (BET). The electrochemically synthesized pure-phase sample was tested for the adsorption of a model analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug, Ibuprofen, which was quantified by UV-Vis and 13C NMR spectroscopy. The presence of the drug loaded on the material was also verified by FTIR, TG, SEM, and BET analyses.