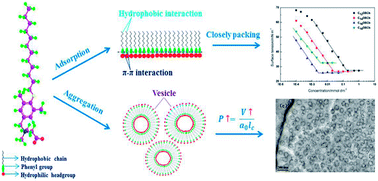
A series of carboxybetaine surfactants, 2-((4-(alkoxy)-3,5-dimethylbenzyl)dimethyl-ammonio)acetate (CnOBCb, where n represents the hydrocarbon chain length of 12, 14, 16 and 18), were synthesized by an efficient and high-yield route for the first time. The surface activities and aggregation behavior of CnOBCb in aqueous solution were investigated by equilibrium surface tension, interfacial tension, steady-state fluorescence, dynamic light scattering (DLS), cryogenic transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM) and negative-staining transmission electron microscopy (TEM) measurements. In comparison with conventional N-alkylbetaine surfactants (CnCb), the CnOBCb species, with a phenyl group introduced in the hydrophobic tail, exhibited excellent surface activities, including lower critical micelle concentration (cmc), lower surface tension and stronger adsorption tendency at an air/water interface. CnOBCb also displayed high efficiency in reducing the toluene/water interfacial tension, with C12OBCb achieving an ultralow interfacial tension (10−3 mN m−1) at concentrations from 0.2 to 1 mmol dm−3. The fluorescence intensity ratio and the scattering intensity in DLS measurements changed remarkably at concentrations around the cmc. Furthermore, the CnOBCb species spontaneously formed vesicles above the cmc in aqueous solution, and the size of the aggregates increased with increasing surfactant concentrations. Flooding experiments showed that CnOBCb could effectively improve oil recovery by 7.85–10.55%.