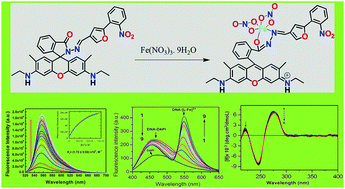
A novel di-coordinating rhodamine-based chemosensor, HL with NO donor atoms, selectively and rapidly recognizes Fe3+ in the presence of all biologically relevant as well as toxic metal ions and numerous anions and also with other reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. It exhibits a lower detection limit (0.17 μM) and comparatively higher formation constant (Kf = 1.72 × 104 M−1). The DNA-binding properties of [LFe(NO3)2]+ complex have been comprehensively studied by using UV-Vis, fluorescence, and optical melting studies and circular dichroism, which clearly indicate that [LFe(NO3)2]+ interacts with DNA via a groove binding mode. In particular, competition experiments with Hoechst and DAPI constitute firm evidence for this binding mode, and clearly rule out intercalation. The negative ΔG0 and positive ΔS0 values obtained from a calorimetric technique confirm the spontaneity of the binding of [LFe(NO3)2]+ with DNA. The resulting [LFe(NO3)2]+/DNA composite material could be a valuable candidate for future photonics and/or biological applications.