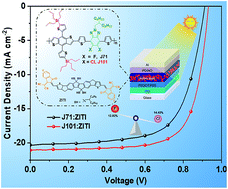
Realizing the triple functions of simultaneously improved open circuit voltage (Voc), short circuit current density (Jsc) and fill factor (FF) enabled by material design is a vital challenge for achieving efficient and stable polymer solar cells (PSCs). Herein, we developed a new wide-bandgap donor–acceptor (D–A) copolymer, J101, with a down-shifted highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) level by chlorine substitution on its 2-alkyl-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole (BTz) unit. The PSCs fabricated by combining the J101 donor with the indenoindene-containing fused-ring electron acceptor ZITI demonstrated a remarkable power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 14.43% with a high Voc of 0.937 V, a high Jsc of 21.25 mA cm−2 and a high FF of 72.48%, benefitting from the low HOMO level of the donor, suitable nanoscale morphology, efficient charge transport properties and reduced recombination losses. Furthermore, semitransparent PSCs based on the optimized J101:ZITI blend exhibited the best PCE of 11.04% with an average visible transmittance (AVT) of 21.69%. This work demonstrates that the chlorine substituted BTz unit is an excellent electron-accepting building block for high-performance opaque and semitransparent PSCs.