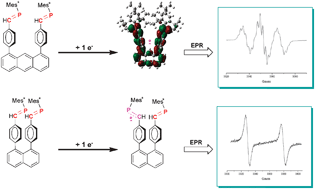
Two molecules containing two phenylphosphaalkene moieties linked by an anthracene (1) or by a naphthalene (2) ring have been synthesized and their crystal structures have been determined. While electrochemical measurements show that these two systems are easily reduced, EPR spectra indicate that, at room temperature, the electronic structures of the two reduction compounds 1˙− and 2˙− are quite different. In 1˙−, in good accordance with DFT predictions, the unpaired electron is delocalized on the full molecule while in 2˙− it is confined on a single phosphaalkene moiety. This difference is attributed to the short distance between the two phenylphosphaalkene groups in 2˙− which hinders their reorientation after addition of an electron. The role of this motion is consistent with the fact that two additional paramagnetic species are detected at 145 K: the dianion 22− characterized by a rather small exchange coupling constant and the radical monoanion 2*˙− resulting from the formation of a one electron P–P bond. These two species are probably reaction intermediates which can lead to the formation of biphosphane.