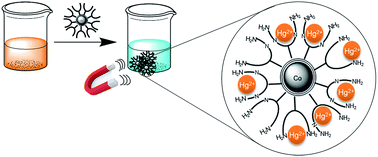
A facile and efficient way to decontaminate mercury(II) polluted water with the aid of magnetic, highly stable and recyclable carbon coated cobalt (Co/C) nanoparticles is reported. Comparing non-functionalised Co/C nanomagnets with particles that were functionalised with amino moieties, the latter one proved to be more effective for scavenging mercury with respect to extraction capacity and recyclability. A novel nanoparticle–poly(ethyleneimine) hybrid (Co/C–PEI) prepared by direct ring opening polymerization of aziridine initiated by an amine functionalised nanoparticle surface led to a high capacity material (10 mmol amino groups per g nanomaterial) and thus proved to be the best material for scavenging toxic mercury at relevant concentrations (mg L−1/μg L−1) for at least 6 consecutive cycles. On a large-scale, 20 L of drinking water with an initial Hg2+ concentration of 30 μg L−1 can be decontaminated to the level acceptable for drinking water (≤2 μg L−1) with just 60 mg of Co/C–PEI particles.