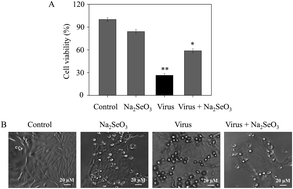
The high variability of influenza viruses has made it more difficult for people to cope with influenza. When antigen transformation occurs, even new influenza without preventive vaccines may be produced, which poses a great threat to human health. Selenium is an essential trace element in humans and mammals, and has many biological activities. It has attracted people's research interest in recent years. In this study, MDCK cells were used as a model to observe the effect of sodium selenite on H1N1 influenza virus. Our research showed that sodium selenite (Na2SeO3) has an anti-influenza H1N1 virus effect, and the anti-viral effect of sodium selenite was further demonstrated by caspase-3, AKT, MAPK and p53 signaling pathways. The investigations of the mechanism revealed that the sodium selenite could block H1N1 influenza from infecting MDCK cells through inhibiting the production of ROS. The results demonstrate that selenium supplementation may provide a feasible approach to inhibit the infection of H1N1 influenza virus.