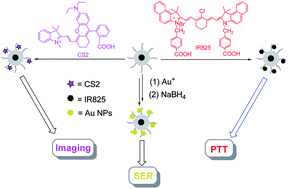
In this work, iron-catalyzed atom transfer radical polymerization with activators generated by electron transfer (AGET ATRP) of poly(ethylene glycol) monomethyl ether methacrylate (PEGMA) and 2-((ethoxycarbonothioyl)thio)ethyl methacrylate (ETCEMA) followed by reduction were performed to modify Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) for introducing thiol groups on the surface of the NPs. Gold NPs and two near infra-red (NIR) organic dyes with different quantum yields were covalently fixed into the polymer shells independently to afford magnetic NPs with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), NIR fluorescence imaging and photo-thermal therapy (PTT) functionalities, respectively. In addition, all of these NPs are able to display as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) because of the existence of the paramagnetic Fe3O4 cores.