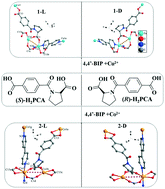
Among various chiral compounds, amide derivatives modified from amino acids are attractive chiral synthons in the synthesis of homochiral metal–organic frameworks. Herein, a pair of proline derivatives, (S)-1-(4-carboxybenzoyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid ((S)-H2PCA) and (R)-1-(4-carboxybenzoyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid ((R)-H2PCA), were designed and synthesized through incorporating a proline unit into 1,4-dicarboxybenzene. Under solvothermal conditions, (S)-H2PCA and (R)-H2PCA further reacted with 4,4′-bipyridine (4,4′-BIP), Cu(II) and Co(II) ions to obtain four enantiomeric compounds, [Cu((S)-PCA)(4,4′-BIP)]·DEF·H2O(1-L), [Cu((R)-PCA)(4,4′-BIP)]·DEF·H2O(1-D), [Co((S)-PCA)(4,4′-BIP)]·1.5H2O (2-L) and [Co((R)-PCA)(4,4′-BIP)]·1.5H2O (2-D) (DEF = N,N-diethyl formamide). Although all compounds have pillared-layer frameworks with 6-connected pcu nets, their structural motifs are still very different. The frameworks of 1-L and 1-D are non-interpenetration structures containing two kinds of helical chains, while 2-L and 2-D are 2-fold interpenetration frameworks with only one kind of helical chain. Furthermore, their solid-state CD spectra, semi-conductive properties and photocatalytic behaviors were also investigated. The present work provides a promising method to design and synthesize homochiral MOFs with helical structures through semirigid (S)-H2PCA and (R)-H2PCA.