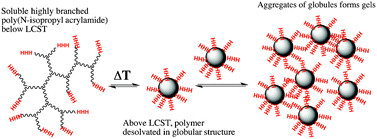
Highly branched poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) was prepared with either carboxylic acid (HB-PNIPAM-COOH) or trihistidine (HB-PNIPAM-3His) end groups. The triHis peptide was linked to the polymer by the N-terminus leaving the C-terminus as the ultimate chain end functionality. The presence of the triHis end groups altered the pH responsive behaviour of the polymers so that the HB-PNIPAM-3His polymer had elevated cloud points at both low and high pH, compared to pH 5.5, whereas the cloud points of HB-PNIPAM-COOH aqueous solutions increased as pH increased. Above the cloud point HB-PNIPAM-COOH formed colloidally stable dispersions but the HB-PNIPAM-3His flocculated. However, both polymers formed gels above the cloud point at concentrations of 2.5 weight percent. The addition of triHis end groups had the effect of decreasing the gel temperature and both systems provided gels with storage moduli of 103 to 104 Pa.