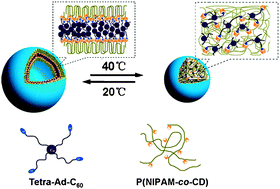
A thermo-responsive copolymer, P(NIPAM-coco-CD), containing β-cyclodextrin as classical host molecule to form highly stable host–guest complexes with 1-adamantane derivatives, was designed and synthesized. The compound tetra-Ad-C6060 with a fullerene[60] moiety and four adamantyl heads was designed as a hydrophobic guest molecule. In aqueous solution, P(NIPAM-coco-CD) and tetra-Ad-C6060 could easily form supramolecular complex by self-assembly of β-cyclodextrin and adamantane, and the supramolecular complex could exist stably as vesicles in ambient environment. Furthermore, the morphology of the supramolecular complex could also be switched reversibly by the change of temperature around the lower critical solution temperature (LCST) of P(NIPAM-coco-CD). When temperature was changed around the LCST, vesicles and nano-spheres formed by supramolecular complex could transform reversibly. Due to the presence of the fullerene moieties, the supramolecular complex exhibited excellent ability to scavenge hydroxyl radicals of biological system; furthermore, the antioxidative property could be affected obviously by the change of temperature owing to the thermo-response property of P(NIPAM-coco-CD) moiety.