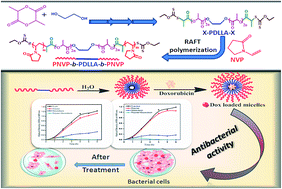
A series of ABA type well-defined amphiphilic poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone) (PNVP)-b-poly(D,L-lactide)-b-PNVP triblock copolymers have been synthesized via the combination of ring opening polymerization and xanthate-mediated reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization, and analyzed by 1H NMR spectroscopy and gel permeation chromatography. Aggregation properties of these amphiphilic triblock copolymers have been revealed by fluorescence spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering, and supported by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Doxorubicin (DOX) has successfully been loaded into the block copolymer micelles with a loading efficiency of 37.5%. DOX-loaded PNVP51-b-PDLLA48-b-PNVP51 block copolymer showed sustained release within 36 h. Antibacterial properties of DOX-loaded micelles have been found to be significantly effective with respect to free DOX in terms of minimum inhibitory concentration, disk diffusion assay, growth curve, bacterial reduction and enzymatic assay based on in vitro studies.