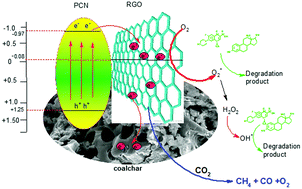
Herein, we report the synthesis of a metal-free coal-char supported polymeric g-C3N4/RGO (RPC) nano-photocatalyst for the efficient solar powered degradation of the noxious emerging pollutants ciprofloxacin (CIF) & β-estradiol (ESD) and conversion of CO2 into CH4, CO & O2. RPC shows good photocatalytic and adsorption activity owing to its high surface area and reduced charge recombination rate. The photodegradation results of the treated water sample were investigated in terms of reaction kinetics, active species trapping experiments, high resolution mass spectrometry (HR-MS) and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) analysis. The higher solar photoactivity is attributed to the higher surface area, higher visible absorption, charge transfer, and reduced recombination. The superoxide radical anions were found to be the major active species in photodegradation, which is also supported by the band structure analysis. The catalytic activity is highly enhanced by the addition of H2O2, O2 and O3 as they facilitate the formation of radicals. The possible degradation pathways for the degradation of CIF and ESD have been proposed. This work shows promising solar-active metal-free photocatalysts for efficient environmental remediation and CO2 conversion to fuels.