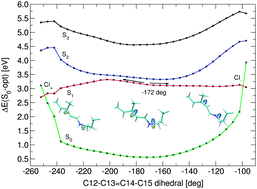
Structure and excited state isomerisation pathway of retinal in the channelrhodopsin chimera C1C2 have been investigated with combined quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical (QM/MM) techniques, applying CD-MS-CASPT2//CASSCF and DFT-MRCI quantum methods. The absorbing S1 state is of 1Bu-like character, and the second excited S2 state is dominated by HOMO–LUMO double excitation with small oscillator strength. Upon photoexcitation and torsion along the reactive C13![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C14 double bond we observe bond length equalisation and a two-path deactivation mechanism in positive and negative torsion directions. The computed path is barrierless in positive direction while a small barrier exists for the opposite side. Comparative protonation studies suggest a charged glutamate E162 residue, with computed resonance Raman data in valuable agreement with experimental channelrhodopsin-2 data. The two negatively charged counter-ions and a positive lysine residue close to the retinal Schiff base terminus have the largest influence on the chromophore absorption wavelength.
C14 double bond we observe bond length equalisation and a two-path deactivation mechanism in positive and negative torsion directions. The computed path is barrierless in positive direction while a small barrier exists for the opposite side. Comparative protonation studies suggest a charged glutamate E162 residue, with computed resonance Raman data in valuable agreement with experimental channelrhodopsin-2 data. The two negatively charged counter-ions and a positive lysine residue close to the retinal Schiff base terminus have the largest influence on the chromophore absorption wavelength.