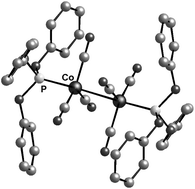
The dinuclear complex [Co2(CO)6{P(OPh)3}2] (2) has been synthesised and was fully characterised. The solid state structure revealed a trans diaxial geometry, no bridging carbonyls, and Co–Co and Co–P bond lengths of 2.6722(4) and 2.1224(4) Å, respectively. Catalysed hydroformylation of 1-pentene with 2 was attempted at temperatures in the range 120 to 210 °C and pressures between 34 and 80 bar. High pressure spectroscopy (HP-IR and HP-NMR) was used to detect hydride intermediates. High pressure infrared (HP-IR) studies revealed the formation of [HCo(CO)3P(OPh)3] (4) at ca. 110 °C, but at higher temperatures absorption bands corresponding to [HCo(CO)4] (3) were observed. The hydride intermediate 4 has also been synthesised and characterised. Upon increased ligand concentration, HP-IR studies showed the formation of new carbonyl absorption bands due to a higher substituted cobalt carbonyl complex-[HCo(CO)2{P(OPh)3}2] (5), which is believed to be catalytically less active. Complex 5 has been synthesised independently and was fully characterised. A low temperature crystal structural study of 5 revealed a trigonal bipyramidal structure with a trans H–Co–CO arrangement and two equatorial phosphite ligands, the Co–P bond lengths being 2.1093(8) and 2.1076(8) Å, respectively.