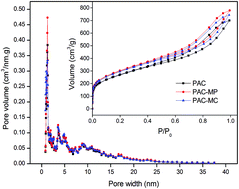
Phragmites australis carbon (PAC) was produced from Phragmites australis by phosphoric acid (H3PO4) activation. To achieve a better amoxicillin (AMX) adsorption performance, manganous dihydrogen phosphate (Mn(H2PO4)2) and manganese chloride (MnCl2) were impregnated, producing PAC-MP and PAC-MC, respectively. Adsorption studies were carried out in different initial AMX concentration (15–100 mg L−1), pH (2–10) and contact time (0–60 h) to evaluate AMX adsorption performance and mechanisms. The adsorption isotherms well agreed with the Langmuir model for the three adsorbents. The maximum AMX adsorption capacity on PAC, PAC-MP and PAC-MC was 110, 132 and 122 mg g−1, respectively. Solution pH had a strong influence on AMX adsorption. For kinetic results, a significant desorption phenomenon was observed. Several possible mechanisms were elaborated which include electrostatic interaction, complexation and degradation of AMX molecules. On the whole, Mn-impregnated PAC showed superior AMX removal efficiency, which presents a promising modification method for activated carbon in the treatment of AMX containing wastewater.