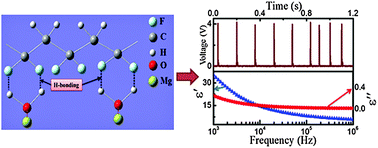
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) films are filled with various mass fractions (wt%) of hydrated metal salt (MgCl2·6H2O) (Mg-salt) to fabricate high performance piezoelectric energy harvesters (PEHs). They deliver up to 4 V of open circuit voltage by simply repeated human finger imparting (under a pressure of ∼4.45 kPa) and also generate sufficient power to turn on at least ten commercial blue light emitting diodes (LEDs) instantly. The enhanced piezo-response is attributed to the combined effect of the change in the inherent dipole moment of the electroactive phase containing PVDF itself and H-bonding arising between the Mg-salt filler and PVDF via electrostatic interactions. Furthermore, it also successfully charged the capacitors, signifying practical applicability as a piezoelectric based energy harvester power source. UV-visible optical absorption spectral analysis revealed the possibility to estimate a change in the optical band gap value at different concentrations of Mg-salt filler added PVDF films that possess a useful methodology where the Mg-salt can be used as an optical probe. In addition dielectric properties have been studied to understand the role of molecular kinetic and interfacial polarization occurs in H-bond PVDF films at different applied frequencies at room temperature.