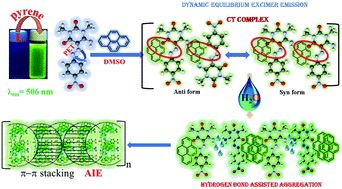
Single crystal X-ray structurally characterized azo-uracil derivative (L) is explored for the selective detection of pyrene via aggregation-induced emission (AIE) with 99-fold fluorescence enhancement. In the presence of pyrene, non-fluorescent L emits green light and allows pyrene detection to as low as 3.6 × 10−9 M. Three model probes (L1, L2 and L3) were employed to support the proposed sensing mechanism. Further, silica-immobilized L efficiently removes pyrene from its reservoir.