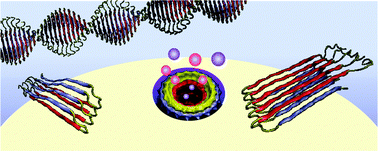
The current paradigm in the amyloid hypothesis brands small β-amyloid (Aβ) oligomers as the toxic species in Alzheimer's disease (AD). These oligomers are fibril-like; contain β-sheet structure, and present exposed hydrophobic surface. Oligomers with this motif are capable of penetrating the cell membrane, gathering to form toxic ion channels. Current agents suppressing precursor Aβ cleavage have only met partial success; and to date, those targeting the