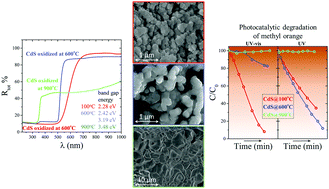
A cadmium sulfide nanopowder was precipitated from water-based precursors and oxidized in air at temperatures ranging from 100 to 900 °C. CdS and the oxidized powders were examined by means of XRD, SEM, EDX, DTA/TG, spectrophotometry, and photocatalytic tests. XRD analysis revealed that CdS had crystallized as a mixture of cubic and hexagonal polymorphs and no changes in its composition were found below 400 °C. At higher temperatures, different oxidized phases belonging to the Cd–O–S system is observed. The appearances of Cd(S2O7) and CdSO4 at 400 °C is accompanied by an increase in the crystallinity. Cd5S3O6, Cd3SO6, and CdO appear at 500, 600, and 800 °C, respectively. SEM observations showed that oxidation leads to a gradual increase in the size of the CdS nanoparticles from 10 nm to more than 3.5 μm at 800 °C. The fundamental absorption edge is present in the visible range of light up to 700 °C, accompanied by the edge in the UV range, which appears at 600 °C. Based on the zeta potential measurements a representative of anionic dyes – methyl orange, was chosen for the photocatalytic experiments under UV and UV-vis light. For the first time, the incredible photoactivity of the oxidized CdS was demonstrated. It was shown that both Cd5S3O6 and Cd3SO6 yield unique photoactivities in the UV range.