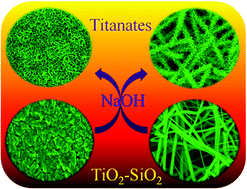
We report a low temperature alkali-mediated conversion of nanofiber-and rice grain-shaped TiO2–SiO2 composites into highly anisotropic fiber (decorated with thorn-like features on surfaces)/sponge-shaped titanates of the formula Na2−xHxTi2O4(OH)2. The titanates were thoroughly characterized by spectroscopy and microscopy. Control experiments with the respective TiO2 analogues revealed that the unique open and highly porous morphologies were the result of structural rearrangement of TiO2 coupled with the in situleaching of SiO2 from the composites by the alkali. Effect of concentration of the alkali and the reaction temperature on the morphology of the titanates was also probed. Evolution of the unique morphologies from the respective starting materials was studied by scanning electron microscopy analyses of the systematically withdrawn samples during the course of the reaction. The materials utilized in dye-sensitized solar cells showed excellent photovoltaic parameters amongst the category of titanates.