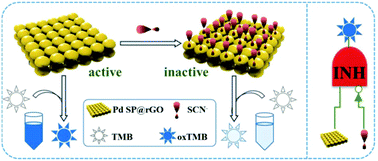
In this work, a novel convenient colorimetric method for sensitive detection of thiocyanate (SCN−) has been developed based on its suppression of the oxidase-like activity of palladium square nanoplates on reduced graphene oxide (Pd SP@rGO). SCN− can be adsorbed onto the surface of Pd SP@rGO via binding with Pd atoms and blocks the active sites that mimic oxidase, thus inhibiting the corresponding chromogenic reaction of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine, which has been comprehensively revealed by the UV-vis spectra and X-ray photoelectron spectra. The color fading exhibits SCN− concentration-dependent behavior and can be easily recorded by either UV-vis spectroscopy or naked-eye observation. Therefore, both quantitative detection via measurement of the decrease in absorbance and visual detection of SCN− can be achieved. Owing to the intrinsic amplification of signals by the oxidase-like activity of Pd SP@rGO without resorting to unstable and destructive H2O2, this assay is straightforward, robust and sensitive enough for the detection of SCN− in real samples. Furthermore, an “INH” logic gate is rationally constructed based on the proposed colorimetric SCN− sensor.