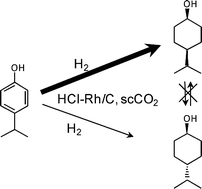
Hydrogenation behavior of 4-isopropylphenol to 4-isopropylcyclohexanol over activated carbon-supported rhodium catalysts in supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) at 313 K was studied in a batch reactor and the results were compared with those in 2-propanol. Higher yields of cis-4-isopropylcyclohexanol were obtained in scCO2 than in 2-propanol, and the formation of a byproduct, isopropylcyclohexane, was suppressed in scCO2. The catalyst modification with hydrochloric or phosphoric acid enhanced the yield of cis-4-isopropylcyclohexanol in both scCO2 and 2-propanol solvents. Kinetic analyses of the reaction profiles revealed higher reaction rates in scCO2 than those in 2-propanol for the 4-isopropylcyclohexanol formation both by the direct hydrogenation of 4-isopropylphenol and by the consecutive hydrogenation of 4-isopropylcyclohexanone, and also revealed that the addition of hydrochloric acid increased the consecutive hydrogenation rate of 4-isopropylcyclohexanone to cis-4-isopropylcyclohexanol, which reduced the total reaction time needed for the complete hydrogenation of 4-isopropylphenol to 4-isopropylcyclohexanol.