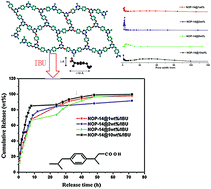
A novel set of nanoporous organic polytriazines with cyanate ester linkages, termed the NOP-14 series, have been designed and constructed from a new triangular monomer 2,4,6-tris(4-cyanatophenyl)-1,3,5-triazine. Four different concentrations of reactive groups in the same solvent medium, have been employed to allow an easy modulation of pore size. The cyanate ester-bridged networks demonstrates somewhat acceptable biocompatibility as identified by cell viability assays with HeLa cells using an MTT assay, and were used as new matrices for in vitro drug delivery of a model drug ibuprofen (IBU). This kind of nanoscale solid with limited surface areas ranging from 25 to 144 m2 g−1, however, can adsorb around 54 wt% of IBU (IBU/NOP-14 mass ratio 2 : 1, immersion time 24 h), demonstrating that the amount of inserted drug does not depend on the surface areas, but correlates more closely with the pore structure. The release behavior of IBU, depending on the porosities and structure of NOP-14 for host–drug interactions, is even better than that of its analogous PAF-6 as well as MCM-41. This study offers the possibility to facilely engineer pore structures through optimization of reaction conditions to control in vivo fate and also extends the controlled release of drugs to general polymers.