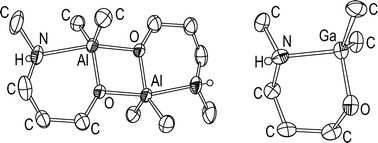
The aminoalcohols MeNH(CH2)2OH (1), tBuNH(CH2)2OH (2), MeNH(CH2)3OH (3), tBuNH(CH2)3OH (4) and MeNHCH2CMe2CH2OAlMe2 (5) have been reacted with AlMe3 to give the five corresponding aminoalkoxides of the general formula RNH–X–AlMe21a–5a (X = organic spacer between N and O). tBuNHCH2CMe2CH2OH (6) reacts with AlMe3 to give [tBuNHCH2CMe2CH2OAlMe2]·AlMe3 (6a·AlMe3). Analogous reactions of the aminoalcohols 1, 2, 3 and 4 with AltBu3, GaMe3 and GatBu3 afforded the corresponding aminoalkoxides of the general formula RNH–X–MR′21b–4b (MR′2 = AltBu2), 1c–4c (MR′2 = GaMe2) and 1d–4d (MR′2 = GatBu2). The compounds were characterised by NMR spectroscopy, elemental analyses and mass spectrometry. Crystal structures were determined for 3a, 5a, 6a·AlMe3, 3c, 3d, 2d and 4d. Compounds 3a and 5a dimerise via Al2O2 rings, while the amino-functions form intramolecular Al–N bonds. Compounds 3c and 3d form monomers with intramolecular Ga–N bonds. Compounds 2d and 4d are dimers via Ga2O2 rings but in contrast to 3a and 5a without formation of intramolecular Ga–N bonds. 6a·AlMe3 also forms a monomeric compound with intramolecular AlN bond and a further AlMe3 unit bonded to the O atom. The dynamic behaviour of 1d and 2d was investigated by variable-temperature NMR spectroscopy. Some compounds have different aggregation in solid and fluid phases.