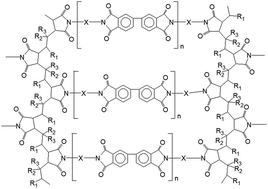
A series of aerogels was fabricated by cross-linking amine end-capped polyimide oligomers with poly(maleic anhydride)s. Poly(maleic anhydride)s are commercially available with various aliphatic side groups and are less costly than other cross-linkers used for polyimide aerogels. Thus they are used here as possible substitutes to form cross-linked polyimide aerogels at a lower cost. The effects of the different side groups of the cross-linkers and oligomer backbone structures on the density, porosity, shrinkage, surface area, morphology, and mechanical properties of the aerogels are discussed. Aerogels with low density (0.12–0.17 g cm−3), high porosity (>88%), high surface area (360–550 m2 g−1), and Young's modulus (2–60 MPa) were produced in the study. The thermal stability and water uptake of the samples were also studied. The aerogels may be potential candidates in a variety of aeronautic and space applications, such as space suit insulation for planetary surface missions, insulation for inflatable structures for habitats, and cryotank insulation for advanced space propulsion systems.