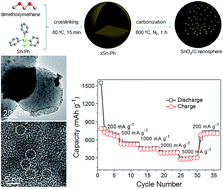
Constructing an electrode integrating ultralow SnO2 size, stable carbon barriers and well-developed pore structure are effective to address the issues of crack and pulverization for SnO2-based electrode during lithiation/delithiation process. But until now, it is still a challenge to exploit simple and robust method to fabricate ultrasmall SnO2 particles embedded in a carbon matrix. Herein, we develop a rapid strategy to prepare SnO2/C nanospheres using a simple Friedel–Crafts crosslinking of triphenyltin chloride for only 15 min and subsequent carbonization. The SnO2/C nanospheres (∼500 nm) have ultrasmall SnO2 particles of 4 nm, which were dispersed in carbon continuous phase. Moreover, the pyrolysis of the polymer during carbonization creates considerable micropores inside the carbon phase and leads to a surface area of 463.3 m2 g−1. When used as electrode materials in a lithium-ion battery, the ultrasmall SnO2 particles can prevent the cracking of the electrode, the carbon continuous phase can act as a buffer to protect SnO2 particles from aggregation, and micropores will supply expansive space for volume change. Thus, the SnO2/C nanosphere exhibits superior electrochemical performance, e.g., the first discharge and charge capacities can reach 1453 and 719 mA h g−1 respectively, and 120 cycles later, its capacity remains 629 mA h g−1, indicating a capacity retention of 87.4% (C120th/C2nd).