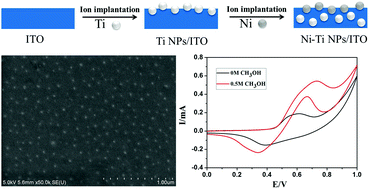
This study has investigated the oxidation of methanol (CH3OH) on a novel bimetallic Ni–Ti nanoparticle-modified indium tin oxide electrode (Ni–Ti NP/ITO) fabricated by the ion implantation method. This has been shown to be a facile, effective and eco-friendly method that could potentially be used to manufacture modified electrodes. The modified electrode exhibits a high electrochemical activity. The techniques of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and cyclic voltammetry (CV) techniques were used to characterize an ITO electrode modified by Ti nanoparticles (Ti NP/ITO), an ITO electrode modified by Ni nanoparticles (Ni NP/ITO) and the morphology and performance of Ni–Ti NP/ITO. The size of the bimetallic Ni–Ti nanoparticles (Ni–Ti NPs) is in the range of 20–30 nm based on SEM analysis. The Ni nanoparticles (Ni NPs) and Ti nanoparticles (Ti NPs) formed on the electrode are in the Ni0 and Ti(IV) metallic states as determined by XPS. The general electrochemical behaviours of the modified electrode were characterized by CV. The Ni–Ti NP/ITO electrode exhibited good electrocatalytic activity for the oxidation of methanol with long-term stability and has possible applications in fuel cells.