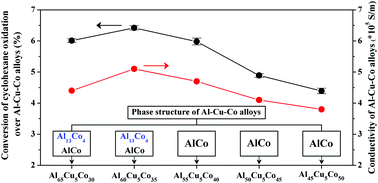
Al–Cu–Co alloys containing different intermetallic compound phases were fabricated by the arc-melting method and used as heterogeneous catalysts for solvent-free cyclohexane oxidation by oxygen. The element composition and bulk structure were characterized by ICP-OES, XRD, SEM, TEM and XPS. Co species were the major active component and a small amount of Cu dissolved in the Al13Co4 phase of the alloy exhibited a synergetic effect on improving the catalytic activity. Cu dissolved in the Al13Co4 phase, a decagonal quasicrystal approximant with a special atomic arrangement structure, could increase the electrical conductivity and accelerate electron transfer during the catalytic oxidation of cyclohexane, and thus improved the catalytic activity of the alloy. Among all the alloys prepared in the present work, the Al60Cu5Co35 alloy exhibited the best catalytic performance with a cyclohexane conversion of 6.4% and a total selectivity of 95.2% to cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone. No significant change in the catalytic activity of the Al60Cu5Co35 alloy was observed after five cycles.