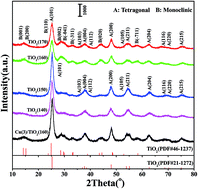
TiO2 nanospheres consisting of flower-like nanopowders were synthesized by a solvothermal method, and Cu/TiO2(T) catalysts were prepared via an impregnation method. Their catalytic performances for the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide (NO) with ammonia (NH3-SCR) were investigated. Their structures, morphology and surface components were characterized via X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy (Raman), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), temperature-programmed desorption of NO (NO-TPD) or O2 (O2-TPD) and temperature-programmed reduction of H2 (H2-TPR) or CO (CO-TPR). The largest specific surface area (236.78 m2 g−1) is obtained for nanosphere TiO2 with flower-like morphology. XPS results show that there are CuO and Cu2O species in Cu(3)/TiO2(T) catalysts. The Cu(3)/TiO2(160) catalyst exhibits the best activity, and its T95 temperature is 170 °C, and the temperature window of NO conversion over 95% is from 170 °C to 310 °C. This is due to the excellent redox properties and the adsorption properties of the catalyst. In situ DRIFTS results demonstrate that Lewis acid sites are involved in NH3-SCR reaction and the adsorption and activation of NH3 play a key role in the process of NH3-SCR over Cu/TiO2(T) catalysts.