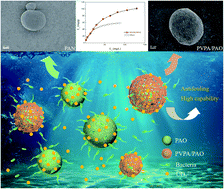
To enhance the anti-biofouling properties and adsorption capability of poly(amidoxime) (PAO), vinylphosphonic acid (VPA, CH2![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH-PO3H2) was polymerized on poly(acrylonitrile) (PAN) surface by plasma technique, followed by amidoximation treatment to convert the cyano group (–C
CH-PO3H2) was polymerized on poly(acrylonitrile) (PAN) surface by plasma technique, followed by amidoximation treatment to convert the cyano group (–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N) into an amidoxime group (AO, –C(NH2)
N) into an amidoxime group (AO, –C(NH2)![[double bond, length as m-dash]](http://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–OH). The obtained poly(vinylphosphonic acid)/PAO (PVPA/PAO) was used as an adsorbent in the uptake of U(VI) from seawater. The effect of environmental conditions on the anti-biofouling property and adsorption capability of PVPA/PAO for U(VI) were studied. Results show that the modified PVPA enhances the anti-biofouling properties and adsorption capability of PAO for U(VI). The adsorption process is well described by the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and reached equilibrium in 24 h. Adsorption isotherms of U(VI) on PVPA/PAO can be well fitted by the Langmuir model, and the maximum adsorption capability was calculated to be 145 mg g−1 at pH 8.2 and 298 K. Experimental results highlight the application of PVPA/PAO in the extraction of U(VI) from seawater.
N–OH). The obtained poly(vinylphosphonic acid)/PAO (PVPA/PAO) was used as an adsorbent in the uptake of U(VI) from seawater. The effect of environmental conditions on the anti-biofouling property and adsorption capability of PVPA/PAO for U(VI) were studied. Results show that the modified PVPA enhances the anti-biofouling properties and adsorption capability of PAO for U(VI). The adsorption process is well described by the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and reached equilibrium in 24 h. Adsorption isotherms of U(VI) on PVPA/PAO can be well fitted by the Langmuir model, and the maximum adsorption capability was calculated to be 145 mg g−1 at pH 8.2 and 298 K. Experimental results highlight the application of PVPA/PAO in the extraction of U(VI) from seawater.