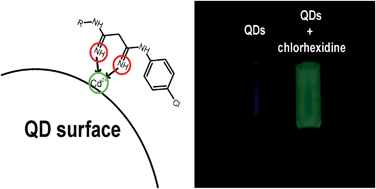
In this work the fluorescence enhancement that water-soluble CdTe quantum dots (QDs) capped with 3-mercaptopropionic acid (MPA) exhibit in the presence of a biguanide compound, chlorhexidine, was investigated. Acting as an electron-donor ligand, chlorhexidine was able to interact with the defects (mid-gap energy traps) on the QD surface improving the surface passivation and the fluorescence emission. The accomplished fluorescence enhancement was used as the sensing strategy for the implementation of an analytical methodology for the determination of chlorhexidine in pharmaceutical formulations. The developed approach was implemented by resorting to fully automated multipumping flow systems, which improved the versatility and analytical potential provided by QDs thereby enabling some of the shortcomings associated with the commonly used batch procedures to be overcome. Different sized QDs were synthesised and evaluated. A chlorhexidine analytical working range for concentrations between 0.05 × 10−3 and 0.5 × 10−3 mol L−1 was verified with a sampling throughput of about 63 samples per hour. The obtained results were in good agreement with those obtained using the reference method (RD% < ±4.77). A mechanism for the enhancing phenomenon is proposed.