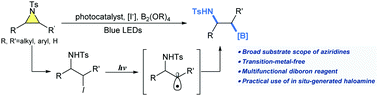
An unprecedented synthetic strategy is devised to generate β-aminoboronic acids from aziridines via a sequential process involving 1,2-iodoamine formation and radical borylation under light irradiation. A variety of aziridines including multiply substituted aziridines have been successfully employed as synthetic precursors, expanding their synthetic utility compared to previous methods. Mechanistic studies suggest that the boron source plays a unique role in the borylation step, and in the formation of haloamine intermediates.