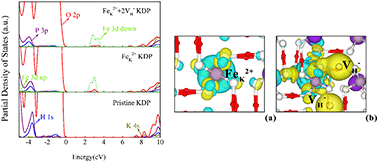
The Fe3+ ion is the most common impurity ion in potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) and can combine with hydrogen vacancies to form cluster defects, which can lead to optical damage of the KDP crystal. In this study, the effect of the FeK2+ + 2VH− cluster on the crystal structure, electronic, and optical properties of KDP crystals were investigated using hybrid density functional theory, and the mechanism of Fe3+ ions lowering the laser-induced damage threshold of the KDP crystal was analyzed. The damage from the FeK2+ + 2VH− cluster defect to the crystal structure of the KDP crystal was found to be greater than that from hydrogen vacancies due to the large lattice relaxation introduced by FeK2+ defects. The FeK2+ defect introduces two defect states (at 2.4 eV and 6.6 eV) into the bandgap of the KDP crystal as well as absorption peaks at around 278 nm in the xy plane. When FeK2+ + 2VH− cluster defects form, hydrogen vacancies induce an increase in charge density around the O atoms bonded to FeK2+, which slightly alters the interaction of the electronic states of the FeK2+ and O atoms. These cluster defects have an influence on the electronic and optical properties via charge transfer in the xy plane in the KDP crystal. This work provides a good suggestion to improve the laser-induced damage threshold of KDP crystals by decreasing the concentration of cluster defects in KDP crystals.