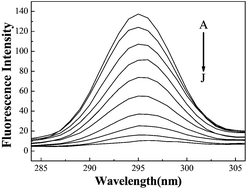
A novel and sensitive method based on the quenching of the fluorescence intensity of functionalized ZnS nanoparticles (NPs) by nevirapine was proposed in this paper. ZnS NPs were synthesized by a hydrothermal method and modified with thioglycolic acid (TGA). The water-soluble modified ZnS NPs were characterized using transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffractometry, zeta potential/particle sizing and photoluminescence spectroscopy. Under the optimum conditions, the relative fluorescence intensity (log(F0/F)) of ZnS NPs is linearly proportional to the nevirapine concentration ranging from 4.6 to 200 μM, and the limit of detection for nevirapine was found to be 0.73 μM. Moreover, the possible quenching mechanism was also investigated. The present method is convenient and suitable for practical applications.