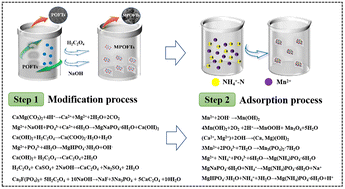
Electrolytic metal manganese wastewater (EMMW) is industrial wastewater produced in the process of producing electrolytic metal manganese, which contains Mn2+ and NH4+–N pollutants. How to deal with low concentrations of Mn2+ and NH4+–N from EMMW is an urgent problem for electrolytic manganese enterprises. In this study, Mn2+ and NH4+–N were removed via adsorption by modified phosphate ore flotation tailings (MPOFTs). The results indicated that the concentration of Mn2+ and NH4+–N in the EMMW decreased from 165 mg L−1 to 0.001 mg L−1 and from 70 mg L−1 to 1.73 mg L−1, respectively, when the solid–liquid ratio of MPOFTs to EMMW was 1 : 200, the reaction temperature was 323 K, the reaction time was 2.5 h and the initial solution pH was 9.0. The adsorption process was more consistent with the pseudo-first-order adsorption kinetic model and Weber's intraparticle diffusion model, and the results showed that this adsorption reaction was an endothermic reaction. This study provided a new research idea for EMMW and POFT treatment and disposal.