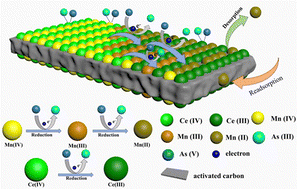
The efficient removal of toxic heavy metal As(III) from water environments has become increasingly urgent due to its adverse health effects. In this study, Mn–Ce oxide-modified activated carbon (Mn–Ce/ACx) composites were synthesized using a simple hydrothermal process and investigated for their As(III) adsorption performance. The Mn–Ce/AC3 composites exhibited exceptional adsorption properties, with high oxidation and adsorption capacity for As(III), owing to their high specific surface area (213.45 m2 g−1) and the presence of surface hydroxyl groups with high affinity. At pH = 7.0, the adsorption capacity of Mn–Ce/AC3 composites for As(III) reached 73.16 mg g−1. Even at very low equilibrium As(III) concentrations, Mn–Ce/AC3 composites could further reduce the concentration to less than 10 μg L−1 at an initial As(III) concentration of 10 mg L−1, which meets WHO standards. Moreover, over a wide pH range of 2–9, Mn–Ce/AC3 composites effectively removed As(III) by oxidation followed by adsorption, indicating that this material is a highly promising adsorbent for the treatment of As(III)-contaminated water.