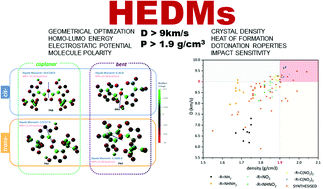
A methodology to design new high energy density materials by means of combining linkage groups and substituted fragments to 1,2,3-triazole-N-oxide series results in 48 novel energetic molecules. The optimized geometry, electrostatic potential, molecular polarity index and HOMO–LUMO orbitals of these molecules were calculated first based on density functional theory (DFT) calculations. And their energetic parameters including the density, heat of formation, detonation properties and impact sensitivity were extensively evaluated. More importantly, the analysis of the electronic structure and detonation properties reveals the structure–property correlations in the 1,2,3-triazole-N-oxide series. The results suggest that the coplanarity of molecular skeleton and electronic conjugation of substituted groups lead to a great impact on the HOF value and lower impact sensitivity. The –C(NO2)3 group derivatives tend to have the most superior detonation properties with zero-close oxygen balance in their structures. These newly designed triazole-N-oxides exhibit moderate impact sensitivities, high density, good heat of formation, and excellent detonation performance, which in cases of TN2 (D = 9.64 km s−1, and P = 42.77 GPa) outperform the current explosive benchmark HMX, making them promising candidates of new environmentally friendly HEDMs. This study convincingly demonstrated the feasibility of the applied strategy of introducing N-oxide and nitrogen-rich groups to bis-triazoles to develop new energetic materials.